How circuit breakers work?

Circuit breakers, essential components in the electrical systems of buildings in Singapore and beyond, function as safety devices designed to prevent electrical overloads and short circuits. By automatically cutting off electrical flow when irregularities are detected, circuit breakers play a crucial role in protecting electrical circuits and reducing the risk of electrical fires.

How does a circuit breaker trip?
A circuit breaker trip occurs when the device detects an anomaly in the electric circuit it services, protecting the circuit's health and functionality.
The core component responsible for this protective measure is the trip unit, an integral part of the circuit breaker designed to automatically shut off electrical flow when it senses conditions that could cause damage or overheating. This essential function safeguards not only the circuit but also the appliances and individuals relying on its services.
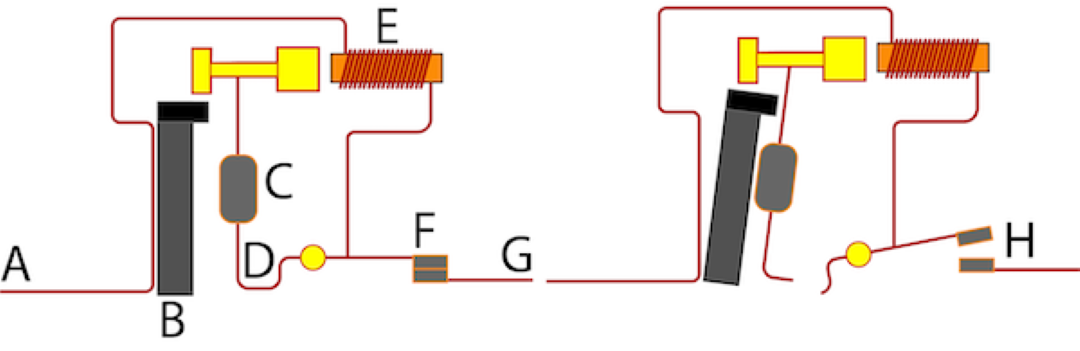
How does a circuit breaker work?
A circuit breaker works as a crucial device in managing electrical circuits by automatically stopping the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit.
The heart of a circuit breaker is its coil wrapped around a metal core which becomes magnetized when electric current flows through it. This magnetic field strength is directly proportional to the current; in abnormal conditions such as short circuits, the magnetic force rapidly increases, triggering the trip unit. This action causes the circuit breaker to break the circuit, thus protecting the electrical system from damage.
Variants like the miniature circuit breaker (MCB) protect against overloads and short circuits, while the residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) is specifically designed to guard against electric shock. Low voltage circuit breakers ensure the safety of lower voltage systems, making circuit breakers an essential safety mechanism in electrical engineering.
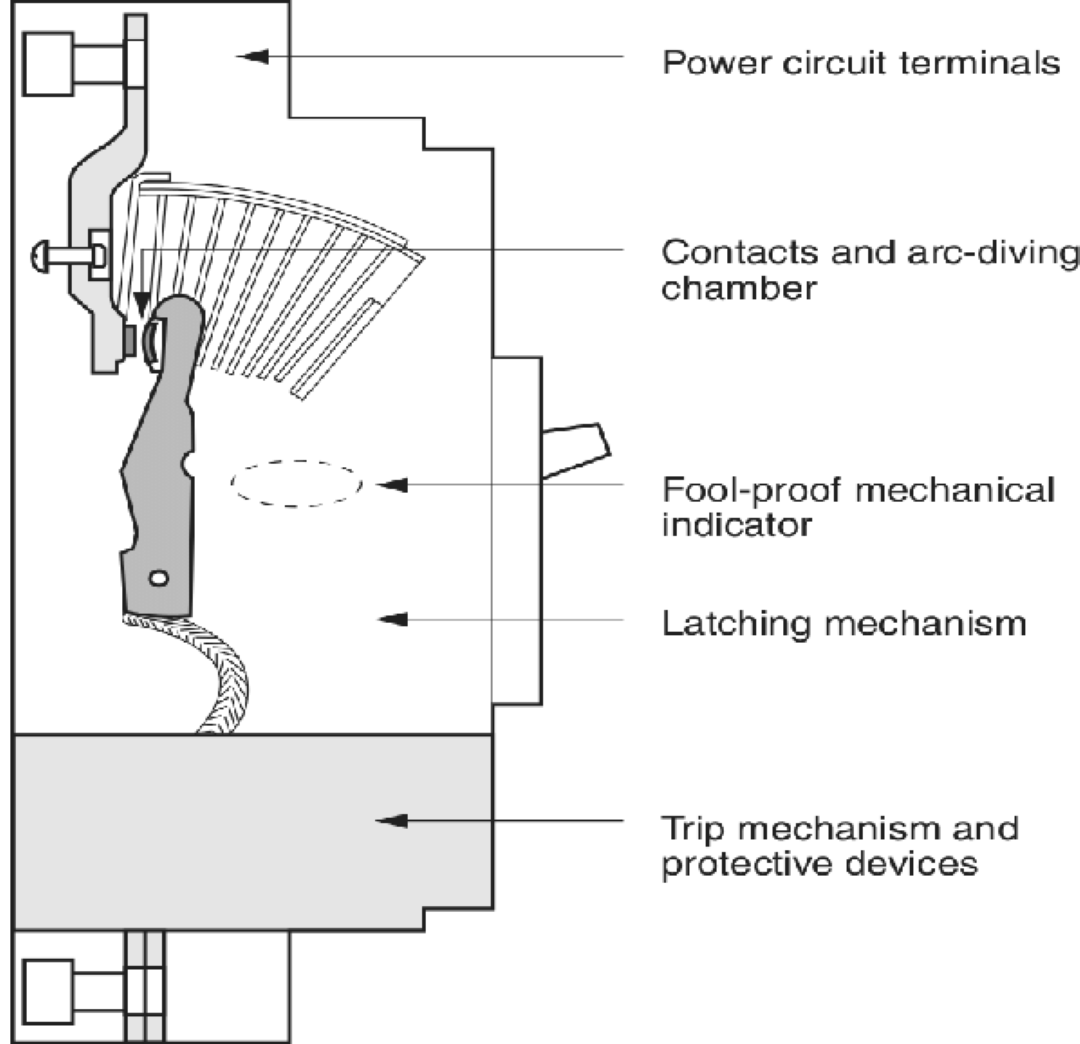
What part of a circuit breaker causes the breaker to trip on a short circuit?
The switch linkage/ contacts of a circuit breaker causes the breaker to trip on a short circuit. This ensures the device's high breaking capacity is utilized effectively to protect the electric circuit.
This operating mechanism is intricately designed to carry the rated current without overheating—thanks to the contacts/switch linkage that can efficiently deliver the load while guarding against power surges or arcs.
When the system experiences too much current (through an electromagnet) or excessive heat (as a strip bends), it activates the switch linkage. This functions then propels the breaker to trip, disconnecting the energy flow and preventing damage.
The circuit breaker is an essential component. They include miniature circuit breakers for low voltage scenarios, residual current circuit breaker for grounding faults, and other protection devices installed in industrial systems.
They operate with the expected precision to offer robust protection by breaking the circuit whenever necessary, based on their trip unit's specifications. This functionality underscores their critical role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.

Will high voltage trip a circuit breaker?
No, high voltage alone will not trip a circuit breaker. A circuit breaker is designed mainly to protect a circuit from overcurrent situations, not directly from high voltage.
The essential function of the device is to cut the power when current exceeds safe levels, preventing potential damage to components and hazards like fires. While high voltage can lead to overcurrent if the circuit is inadequately designed, the breaker trips due to the excessive current rather than the voltage itself.
Its operating mechanism disconnects the circuit from the power source by moving a stationary contact away from another contact, effectively stopping the flow of electricity when it detects overcurrent conditions.
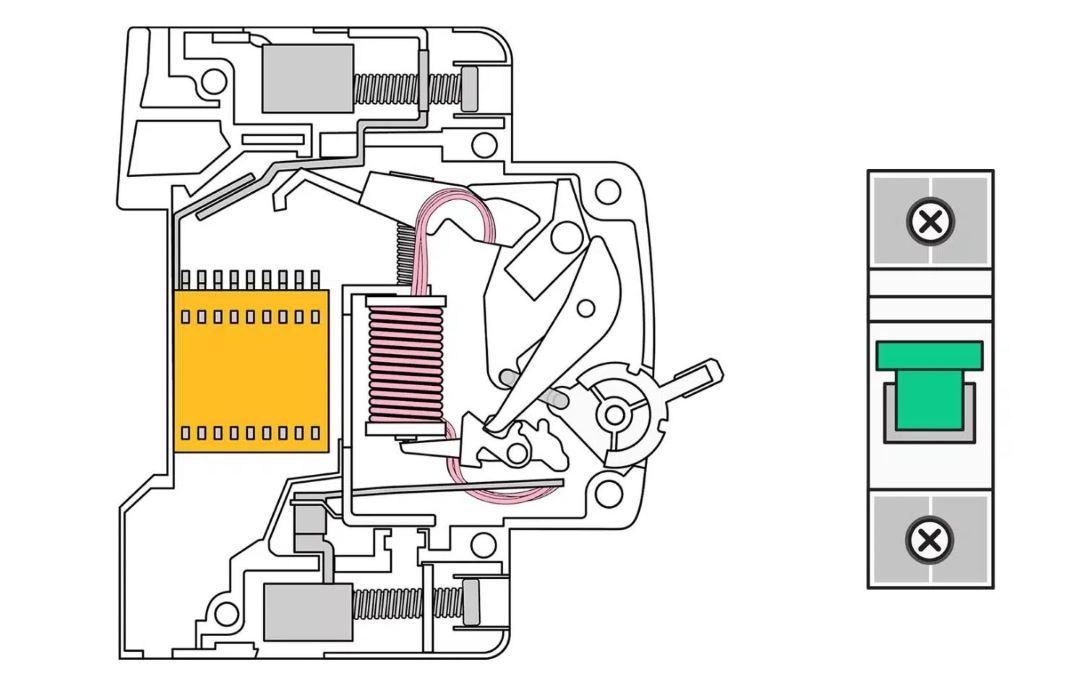
How does a circuit breaker work simple terms?
In simple terms, a circuit breaker works by utilizing a mechanism that automatically interrupts power flow in a circuit whenever it detects an overcurrent, which could potentially cause damage or overheating.
Circuit breakers are essential for both the safety and maintenance of electrical systems. It consists of various components such as coils, which act in response to the flow of too much current, and a motor mechanism that operates the contacts to either carry or break the connection.
Circuit breakers are installed as a more convenient and reliable form of protection compared to fuses, as they can easily be reset after tripping. The circuit breakers' primary function is to prevent energy overload and short circuits, ensuring the phase of the electrical supply is controlled and safe.
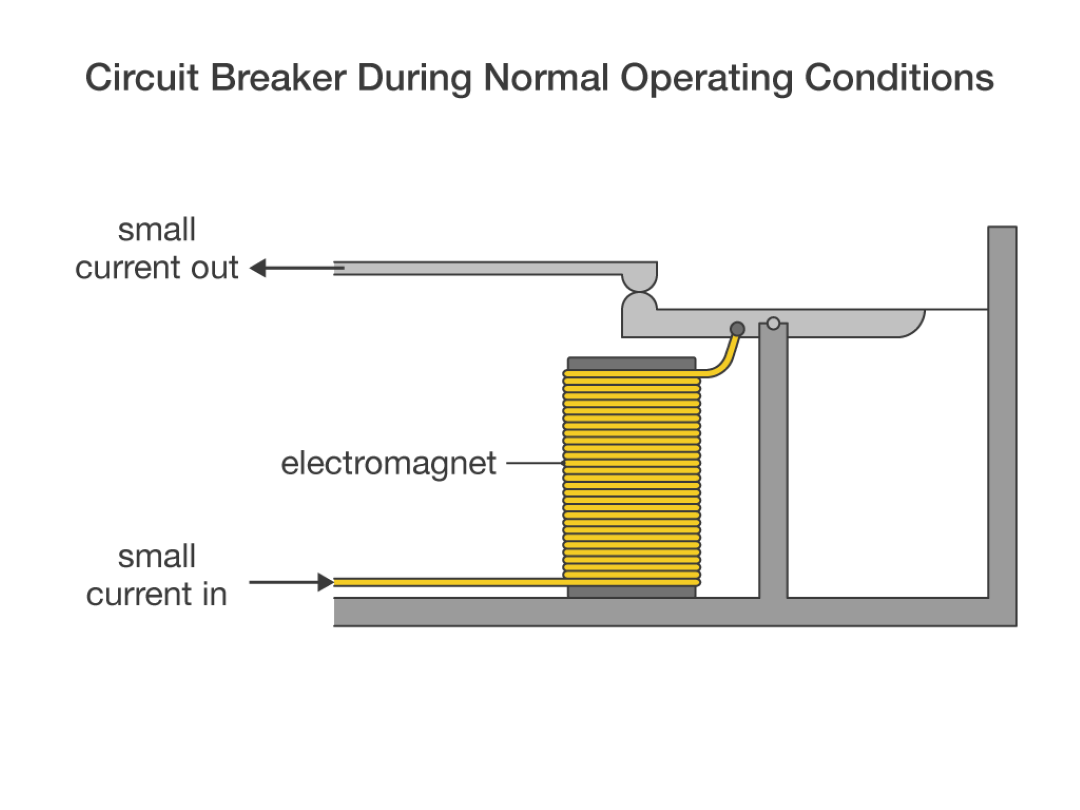
What is the working principle of a circuit breaker?
A circuit breaker operates by automatically turning off the electrical circuit when unexpected conditions occur, such as an overload or a short circuit.
This essential safety mechanism functions by using two types of protection methods: thermal, for overload protection, and magnetic, for short-circuit protection. When a circuit breaker is in the "on" position, electricity can flow from the power supply to the load. However, in the event of an overload or a short circuit, the internal components of the circuit breaker, including a coil or electromagnet and a thermal strip, work in parallel to quickly move the switch linkage to the "off" position, interrupting the power supply and preventing potential damage to the equipment and hazards like fire.
This process aids in ensuring the safety of electrical systems in residences and industries alike. The assistance of different types of circuit breakers, designed for specific applications, ensures that everything from a household light to large industrial equipment operates safely, minimizing the risk of damage and fire spread due to electrical faults.

How do circuit breakers work?
Circuit breakers work by interrupting the electric current when it exceeds its design limitations, therefore preventing the supply of energy to the loads and damage to the circuit.
These devices are essential components in electrical systems, providing vital protection to both household and industrial circuits.
They operate by monitoring the power and electricity flowing through an electric circuit. When the current surpasses the rated current, indicating conditions such as an overload or a short circuit, the trip unit functions to disconnect the flow of energy.
This precise action protects the circuit by immediately halting excess current, thus ensuring short circuit protection and safeguarding the associated equipment.
Overall, the circuit breaker's ability to quickly and effectively break the circuit under dangerous conditions contributes significantly to electrical safety and reliability.

What causes a circuit breaker to trip?
Circuit breakers trip when electrical fault threatens to cause damage to the circuit, and this could be due to an excess of current, power surge, or a faulty component.
In scenarios where an electric circuit experiences overcurrent or voltage fluctuations, which can lead to short circuits, the trip unit acts immediately to protect the system.
Installed within both household and industrial systems, these protection devices are designed to monitor and react quickly to electrical irregularities.
When such faults occur, the circuit breaker switch is activated, disconnecting the energy flow and shielding valuable components and equipment.
This automatic response not only enhances short circuit protection but also prevents potential hazards associated with overloads, ensuring the safe operation and longevity of electrical installations.
Installed in both residential and commercial establishments inside distribution boxes in Singapore and worldwide, this component employs an electromagnet or a thermal mechanism to detect fault conditions. Read our article to understand what is a distribution box (DB box) and how does a power distribution box (DB box) works.
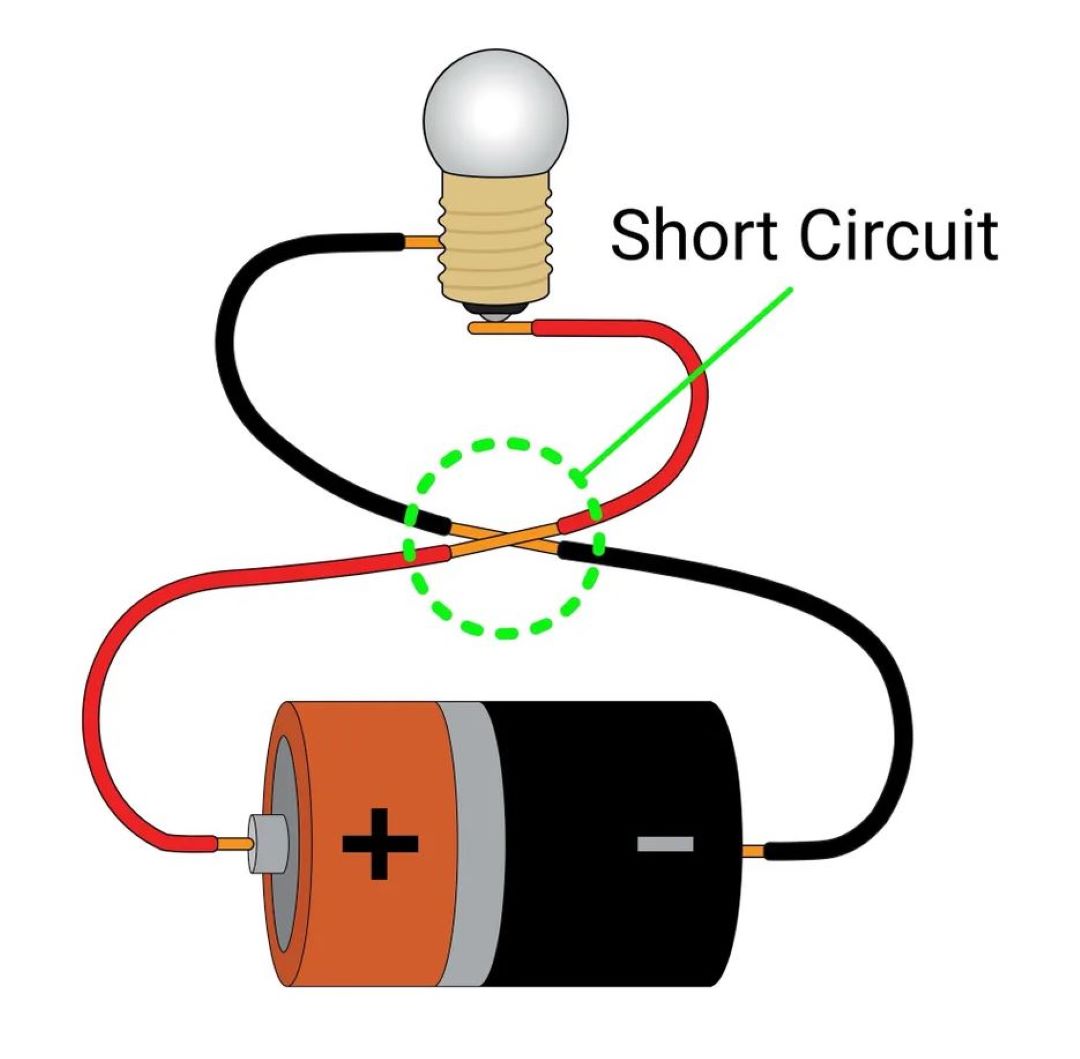
How does a circuit breaker stop electricity?
A circuit breaker stops electricity by automatically disconnecting the circuit when it detects an overload or short circuit.
The working principle involves a power source that supplies energy to an operating mechanism capable of separating the stationary contacts.
When the contacts break, it interrupts the electric current and effectively stops the flow of energy. In instances of overcurrent, the trip unit—an integral part of the circuit breaker's function—activates to provide protection for the electrical system.
Circuit breakers are recognized for their high breaking capacity, ensuring that they can manage significant electrical loads safely without damage. What are the types of circuit breakers?
Installed in various positions within electrical systems, different types of circuit breakers cater to specific needs and configurations, enhancing the overall protection of the structure.
Their reliable operation ensures that electrical installations maintain safety and longevity by swiftly managing unexpected electrical faults.
How do circuit breakers know when to trip?
Circuit breakers know when to trip based on built-in sensing mechanisms that detect abnormal current flow, acting when there is too much current or heat.
These sensitive components are designed to identify fault parameters such as overcurrent or short circuit conditions, triggering the circuit breaker to operate and disconnect the circuit.
The expected performance of a circuit breaker relies on its ability to protect electrical installations and valuable equipment from damage.
By providing a layer of protection, these devices ensure that power sources do not supply excessive current to an electric circuit, thus preventing potential hazards.
With their high breaking capacity, circuit breakers can effectively manage both overload and short circuit situations, safeguarding against overcurrent events.
These protection devices are crucial in maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical systems, ensuring they function safely and reliably over time.