Fire Safety in Electrical Installations
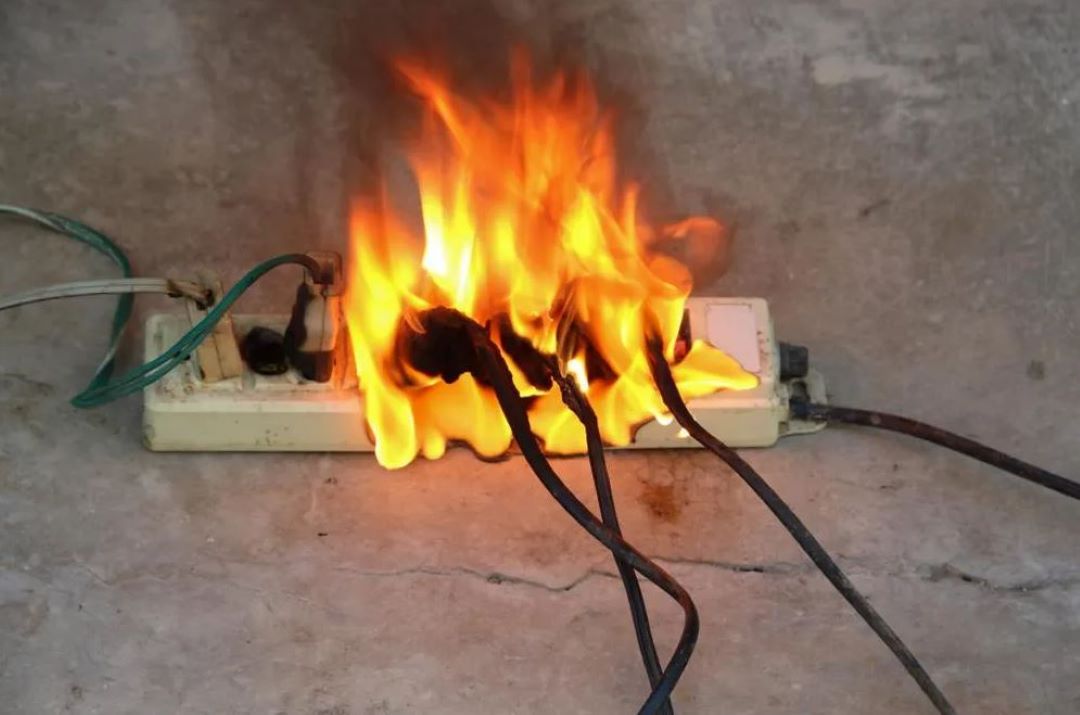

Understanding the significance of fire safety in electrical installations is crucial to preventing devastating electrical fires. Electrical fires can originate from a variety of sources such as faulty electrical cables, malfunctioning cooking equipment, or from a short circuit. To safeguard against such fires, regular electrical inspections are imperative.
Electrical inspections not only help in identifying potential hazards that could lead to a fire but also ensure that appropriate electrical fire extinguishers, such as Class D for electrical fires, are easily accessible. Class D extinguishers are specifically designed toe extinguish fires involving materials that present unique hazards, including the heat and gas released from burning electrical equipment.
Being aware of how to safely extinguish such fires, without causing further damage or risking personal safety, is paramount. Hence, integrating comprehensive electrical safety inspections into fire safety plans helps in mitigating risks and protecting both lives and property from the devastating effects of fire.

How to Prevent Electrical Fires At Home?
At home, you can prevent electrical fires by avoiding overloading at the outlet sockets, keep flammable objects away from electrical outlets and cords, unplug small devices and electrical appliances when not in use. Ensure that your kitchen stove and other heat cooking equipment are never left unattended when in use to avoid instances of burning.
In the case of a gas leak, know how to safely extinguish the gas fire using either a class ABC or AB dry powder fire extinguisher which is suitable for class C fires involving electrical equipment and class D for metal fires. Heat, gas (fuel) and short circuits are common causes for electrical fires, therefore it is essential to conduct regular electrical inspection and maintenance.
In addition, an electrical test can help to prevent electrical fires at home. Learn what are the types of electrical tests conducted to prevent electrical fires.

How to Prevent Electrical Fires In The Workplace?
In the workplace, you can prevent electrical fires by namely adhering to stringent safety protocols concerning conductors, insulation, and the use of electrical devices.
The ignition of flammable materials such as wood, paper, or gas due to damaged insulation on cables, misused extension cords, or short circuits in the electrical circuitry, stands as a significant cause of electrical fires.
Class C fire extinguishers are designed for electrical fires and they should be readily accessible to extinguish fires fueled by electricity without conducting heat. Utilizing an electrical fire class C or carbon dioxide fire extinguisher can efficiently extinguish a fire without leaving harmful residues that could damage electrical equipment. It's essential to shut off power in the event of a fire to prevent the escalation of burning materials.
Organizations should ensure the proper maintenance of electrical equipment, avoid overloading circuits, and use cables that are adequately insulated to withstand the power they carry. Additionally, areas with an explosive atmosphere require special attention to prevent ignition.
According to the fire administration, many workplace fires result from a short circuit or the overheating of electrical components. Implementing regular inspections and encouraging a culture of safety can minimize risks.

How To Practice Electrical Fire Safety In The Workplace?
To practice electrical fire safety in the workplace, it's crucial to understand the specific regulations and guidelines set in place in Singapore.
Implementing an annual comprehensive electrical fire drill/ training, including the use of suitable fire extinguishers and ensuring all personnel are trained in fire safety, is essential to prevent and effectively extinguish electrical fires in the workplace.
In offices, all electrical conductors must be properly insulated to prevent short circuits or electricity leakage, which are primary causes of electricity fire.
Materials such as wood and paper, often found in office environments, must be kept away from electrical outlets and cables to prevent ignition. Similarly, the use of extension cords should be minimized as they can lead to overheating and potentially ignite a fire if used improperly or are damaged.
The use of Class C or AB dry powder fire extinguishers is recommended in areas where an electrical fire could occur, as these are suitable to extinguish fires involving electrical equipment without conducting electricity back to the user.
On construction sites and other on-site locations, maintaining electrical safety requires stringent adherence to Singapore's fire administration guidelines. All electrical equipment should be regularly inspected for damaged insulation and potential flammable gas leaks to prevent explosive atmospheres.
Proper shut-off systems and circuit breakers must be installed to quickly cut power in the event of an emergency, significantly reducing the risk of fire from short circuits or overheating. Cables and electrical materials used on-site must meet the specific classes of fire resistance to prevent rapid spread in case of ignition. Class C or class D fire extinguishers must also be installed throughout the site and shall be inspected annually to ensure that it is not expired.
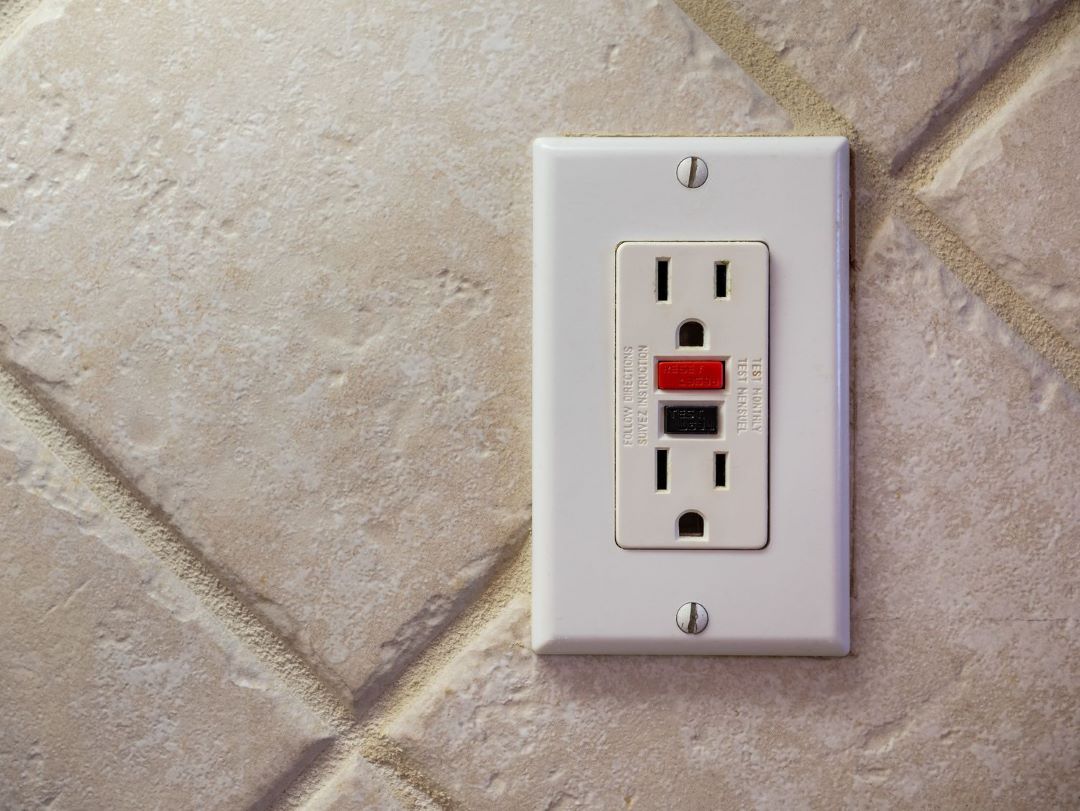

What Device Helps to Prevent Electrical Fires?
The Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) device helps to prevent electrical fires by monitoring the balance of electric current flowing through a circuit.
Should there be any discrepancy that might indicate a short circuit or leakage to ground, the GFCI swiftly break/ cuts off the power supply to prevent fires that can occur due to overheating caused by excess current.
GFCIs are generally installed where electrical circuits may accidentally come into contact with water to protect against sudden changes in current that could not only lead to fires but also pose a significant electrocution hazard.
By continuously checking the power and current's flow in a circuit and comparing the input and output current, the GFCI can determine if there is an abnormality in current flow due to resistance, effectively preventing fires before they can start or ignite.
Which Type of Fire Extinguisher Is Used On Electrical Fires?
The Class C fire extinguisher (Carbon Dioxide Fire Extinguisher) is specifically used on electrical fires, involving equipment and cables that could burn due to high resistance or faulty electricity flow, creating dangerous hot spots.
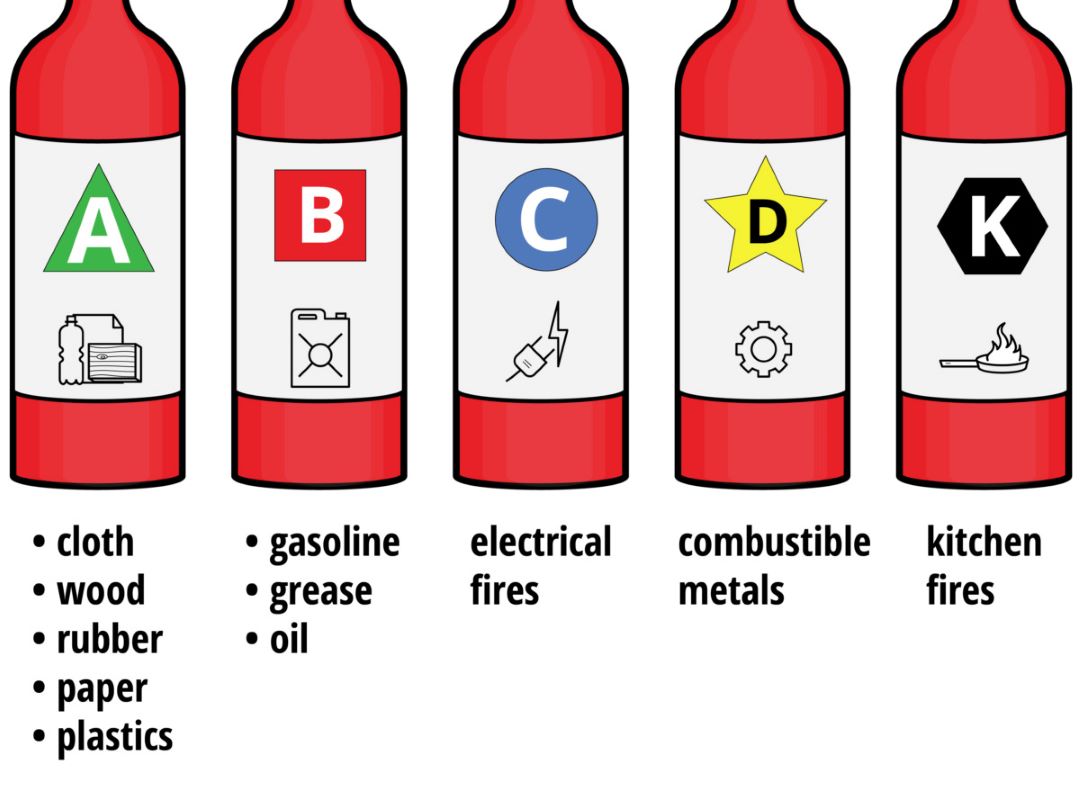
In general, fires are categorized into 5 classes based on the fuel source that the fire burns on. The classes are:
- Class A – Ordinary Combustibles
- Class B – Flammable Liquids & Gases
- Class C – Electrical Fires
- Class D – Combustible Metals
- Class K – Grease/Cooking Fire
For such fires, both CO2 fire extinguisher and the AB dry powder fire extinguisher are highly effective, as they work by eliminating the oxygen around the fire and cutting off the fuel source without leaving damaging residues.
CO2 extinguishers are best suited for environments with flammable liquids and electrical equipment, as they extinguish fires in a controlled manner without causing further damage to sensitive electrical appliances.
On the other hand, AB dry powder fire extinguishers are versatile and can be used on Class B fire (flammable liquids) and Class C fires caused by electrical equipment, but they should not be used on Class D (metal fires) due to the risk of a violent reaction.
These AB dry powder fire extinguishers disrupt the chemical reaction of the fire by coating the fuel source with a thin layer of dust, effectively separating the fuel from the oxygen in the air and halting the fire's chain reaction.
When leaving home for an extended period, it is wise to have these extinguishers readily available and ensure all electrical systems are properly secured to prevent ignition and the rapid spread of fires through flammable materials like wood and gas.

What are the safety precautions for electric fire?
The safety precautions for electric fire prevention include replacing broken plugs and switches to ensure all electrical equipment operates safely. Similarly, keeping electrical wires and electrical cables away from hot and wet surfaces. Develop the habit of switching off appliances after use and removing the plug from the socket minimizes the chance of electerical fires.
For extended safety, turning off the "main" switch when leaving home for a long duration eliminates the risk of electrical burn in the absence of supervision, acting as a comprehensive preventive measure against electrical fires.
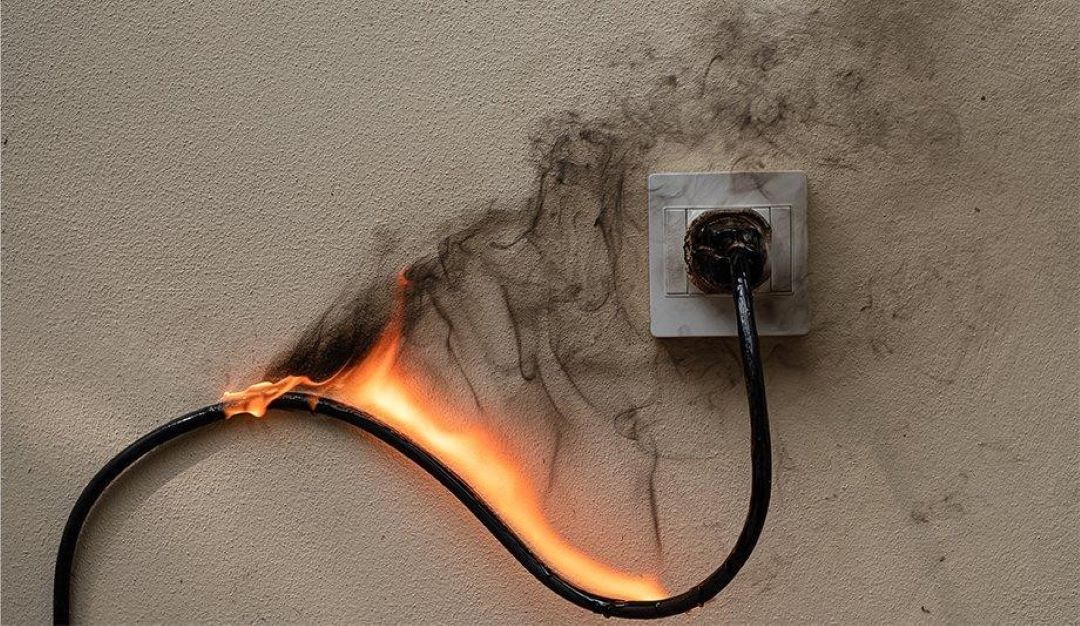

How do you prevent fire from electrical wiring?
You prevent fire from electrical wiring by namely being proactive in the protection and maintenance of your electrical systems.
Generally, it’s essential to guard against overheating, malfunction, and overload, which are common culprits of electrical fires. This can range from ensuring the correct type of protection for each wire and machine to being aware of the signs that equipment is overheated or malfunctioning.
Regular checks can prevent wire fires or wires from becoming heated to an intensity that might lead to flames. Certain chemicals and materials near stoves or other high-heat appliances should be kept away to prevent sparks or flames from coming into contact with flammable substances.
Using electrical equipment correctly, with attention to the capacity and condition of cords and plugs, and ensuring that insulation is intact, can greatly reduce risk. Additionally, making sure that items with resistance and heat-producing capabilities, such as conductors and some appliances, are not overloaded helps to safeguard against fires.
Key to preventing electrical fires is ensuring that equipment is shut down properly when not in use to avoid overheating, and that firefighters are called immediately at the first sign of sparks or flame.
Remember prior to electrical installation, the importance of electrical inspection and preventative measures against electrical failures can dramatically lower the risk of electrical fires, protecting both property and lives.
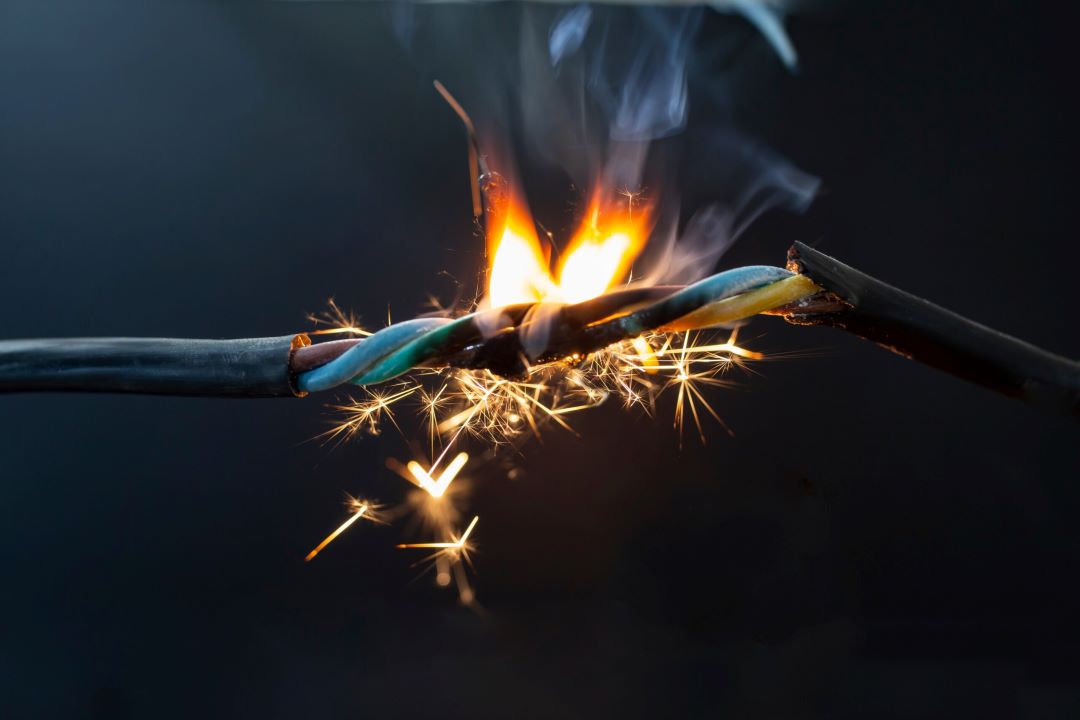

What are the basic electrical fire safety?
The basic electrical fire safety includes never attempting DIY electrical repairs unless you are a trained professional, as improper handling of materials, cables, and circuits can lead to dangerous sparks and accidental flame ignition.
Avoid running extension cords under carpets, rugs, or furniture as this can cause overheating and potentially ignite flammable materials.
Damaged cords or frayed cables should never be used, as these can expose live wires and pose a significant fire risk, especially in an environment with flammable liquids or an explosive atmosphere.
Always unplug machines and power appliances when not in use to reduce the risk of overheating or electrical malfunctions.
Additionally, keeping a fire extinguisher nearby and ensuring firefighters can access the area easily in case of an emergency are essential precautions.
Remember, preventing electrical fires is vital to maintaining safety and protecting oxygen-rich areas from sudden ignition.
What are 5 safety rules for electrical?
The 5 safety rules for electrical include disconnecting the power supply to break the flow of electricity and protect workers from exposure.
It is generally important to prevent any possible feedback by isolating circuits, ensuring that no residual current remains.
Verifying the absence of voltage with proper equipment allows workers to be aware of potential risks and avoid heated components or sparks.
Grounding and short-circuiting the range of conductors reduces hazards and provides added protection against electrical faults.
Additionally, signaling and delimiting the working area help to classify zones where only authorized personnel should enter, ensuring that flammable materials, overloaded electrical cables, and high-voltage equipment are securely managed to maintain safety standards.